APRIL 06, 2018 (Friday)
1.Do CHAPTER 03 TEST. Click the link https://b.socrative.com/login/student/
NOVEMBER 27, 2017 (Monday)
1. Copy the notes below on your Science Notebook, p.144.
- Hydrogen (H) and helium (He) are special elements. Hydrogen, in its neutral form, does not have a neutron. There is only one electron and one proton.
- Helium (He) is different from all of the other elements. It is very stable with only two electrons in its outer orbital (valence shell).
OCTOBER 09, 2017 (Monday)
1. Copy the notes below on your Science Notebook, p.92.
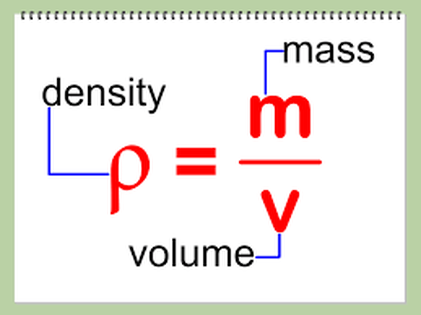
DENSITY
DENSITY – The compactness and size of the molecules or particles of a substance
– The more compact or squished together the molecules are and the more mass the
particles have, the larger the density
Low Density – the atoms are spread far apart from each other
High Density – the atoms are very close to one another
Formula:
DENSITY
DENSITY – The compactness and size of the molecules or particles of a substance
– The more compact or squished together the molecules are and the more mass the
particles have, the larger the density
Low Density – the atoms are spread far apart from each other
High Density – the atoms are very close to one another
Formula:
APRIL 07, 2017 (Friday)
1. Copy the notes below on your Science Notebook, p.176.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
2. Click the link below and complete Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest.
http://tinyurl.com/PBSSpectrum
or
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/gamma/spec_waves.html
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
- An electromagnetic wave consists of a vibrating electric field and a vibrating magnetic field.
- Electromagnetic waves carry radiant energy.
- In an empty space, electromagnetic waves travel at 300,000 km/s, the speed of light.
- Electromagnetic waves travel more slowly in matter with a speed that depends on the material.
- Electromagnetic waves can behave as particles that are called photons.
2. Click the link below and complete Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest.
http://tinyurl.com/PBSSpectrum
or
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/gamma/spec_waves.html
APRIL 06, 2017 (Thursday)
Copy the notes below on your Science Notebook, p.174.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
- Electromagnetic wave is a wave produced by the acceleration of an electric charge and propagated by the periodic variation of intensities of,usually, perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. It can travel through the vacuum of outer space.
- Electromagnetic waves are created by the vibration of an electric charge. This vibration creates a wave which has both an electric and a magnetic component.
- Electromagnetic waves exist with an enormous range of frequencies. This continuous range of frequencies is known as the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Radio waves, Light waves, thermal radiation, X ray, visible light, microwave, infrared, gamma rays etc. are the example of electromagnetic waves. These waves together form the electromagnetic spectrum.
JANUARY 30, 2017 (Monday)
Copy the notes below on your Science Notebook, p.106.
SIX TYPES OF SIMPLE MACHINE
SIX TYPES OF SIMPLE MACHINE
- LEVER
- A lever is a stiff bar that rests on a support called a fulcrum, which lifts or moves loads.
- Examples of Levers: see-saw, stapler, wheelbarrow, nut cracker, tong, tweezers, pliers, bottle opener, scissors, crowbar, baseball bat, clippers, fork, spatula, teeter-totter, rake, can opener.
- PULLEY
- A pulley is a simple machine that uses grooved wheels and a rope to raise, lower or move a load.
- Examples of Pulley: crane, block and tackle, oil derrick, rock climber pulley, steam shovel, flagpole pulley, clothesline pulley, winch, marine pulley, window blinds.
- WHEEL AND AXLE
- A wheel with a rod, called an axle, through its center lifts or moves loads.
- Examples of Wheel and axle: roller skates, gears in watches, pencil sharpener, rotary dial telephone, windmill, casters, egg beater, roller skates, door knobs, bicycle, record player, rolling pin, fan, wagon.
- A wheel with a rod, called an axle, through its center lifts or moves loads.
- Given HOMEWORK: (1) Find and cut two pictures of each type of simple machine from magazine, newspaper, etc. and bring it in class.
DECEMBER 15, 2016 (Thursday)
Copy the notes below on your Science Notebook, p.80.
Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces
Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces
- BALANCED FORCES
- When the forces acting on an object combine and form a net force of zero.
- DO NOT cause a change in the object’s motion.
- UNBALANCED FORCES
- When the forces acting on an object combine and form a net force of something greater than zero.
- DO cause a change in an object’s motion.
- the forces can move opposite of one another OR in the same direction
- The net force has a strength (ex: 20N) and a direction (ex: to the west).
- The direction of the net force is always in the direction of the larger force.
OCTOBER 11, 2016 (Tuesday)
|
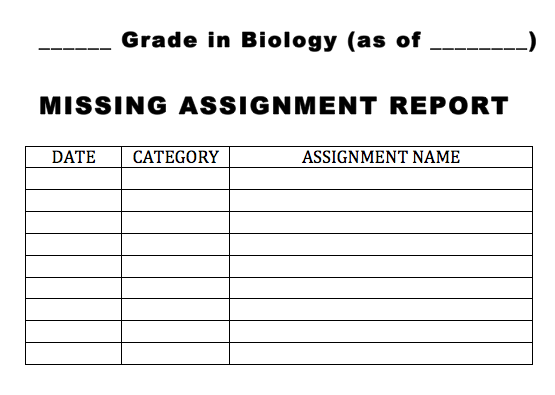
1. Copy the table (the one on the right side) in your Science Notebook, p.28
2. Go to PowerSchool, log in and check your grade. Click this link (https://powerschool.gmcs.k12.nm.us/public/). USERNAME: your student ID number PASSWORD: your birthdate 3. Look for your grade in Integrated Science Class and write it down in your science notebook. 4. Complete the MISSING ASSIGNMENT REPORT TABLE by writing the date, category, and name of your "Missing Assignment." (Choices for Category: ASSESSMENT, CLASSWORK, LAB & PROJECT, HOMEWORK) |